
for Oracle certification, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated . 100% PASS 1Z0-821 Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator exam Today!
Online Oracle 1Z0-821 free dumps demo Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
You are asked to determine user jack’s default login directory. Which command would provide you with useful information?
Answer: A
Explanation: The /etc/passwd contains one entry per line for each user (or user account) of the system. All fields are separated by a colon (:) symbol. Total seven fields as follows.
1. Username: It is used when user logs in. It should be between 1 and 32 characters in length.
2. Password: An x character indicates that encrypted password is stored in /etc/shadow file.
3. User ID (UID): Each user must be assigned a user ID (UID). UID 0 (zero) is reserved for root and UIDs 1-99 are reserved for other predefined accounts. Further UID 100-999 are reserved by system for administrative and system accounts/groups.
4. Group ID (GID): The primary group ID (stored in /etc/group file)
5. User ID Info: The comment field. It allow you to add extra information about the users such as user's full name, phone number etc. This field use by finger command.
6. Home directory: The absolute path to the directory the user will be in when they log in. If this directory does not exists then users directory becomes /
7. Command/shell: The absolute path of a command or shell (/bin/bash). Typically, this is a shell. Please note that it does not have to be a shell.
NEW QUESTION 2
user1 has a disk quota of 0.5 MB. The user attempts to run the following command on a file called .bigfile that is 495 KB in size:
cp bigfile /tmp
Will the command execute successfully?
Answer: A
Explanation: UFS quotas enable system administrators to control the size of file systems. Quotas limit the amount of disk space and the number of inodes, which roughly corresponds to the number of files, that individual users can acquire. For this reason, quotas are especially useful on the file systems where user home directories reside. As a rule, the public and
/tmp file systems usually do not benefit significantly by establishing quotas. Note: The cp command copies files and directories.
NEW QUESTION 3
You wish to edit your crontab file that is located in /var/spool/cron/crontab. What command must you enter to edit this file?
Answer: A
Explanation: The main tool for setting up cron jobs is the crontab command, though this is not available on every Unix variant. Typically under Solaris or Linux one would create a new crontab or edit an existing one, using the command;
crontab -e
Use the ls -l command to verify the contents of the/var/spool/cron/crontabs file.
NEW QUESTION 4
user1, while in his home directory, is attempting to run the following command in his home directory: cp bigfile verybig
The system displays the following error:
cp: cannot create verybig: Disc quota exceeded
Your initial troubleshooting shows that the df -h command indicates he is at 100% capacity. What command would you use to increase the disk space available to the user?
Answer: E
Explanation: ZFS quotas can be set and displayed by using the zfs set and zfs get commands. We can remove the quota restriction by setting to quota to none.
NEW QUESTION 5
You need to set up a local package repository to serve 75 client systems. Multiple clients will being the package repository concurrently and you need to ensure that the local repository performs very well under this heavy load, especially during package intensive operations.
Which option would ensure the best performance of the repository during package-
intensive rations by multiple clients?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 6
You have a ZFS file system named /dbase/oral and you want to guarantee that 10 GB of storage space is available to that dataset for all data, snapshots, and clones.
Which option would you choose?
Answer: D
Explanation: A ZFS reservation is an allocation of disk space from the pool that is guaranteed to be available to a dataset. As such, you cannot reserve disk space for a dataset if that space is not currently available in the pool. The total amount of all outstanding, unconsumed reservations cannot exceed the amount of unused disk space in the pool. ZFS reservations can be set and displayed by using the zfs set and zfs get commands. For example:
# zfs set reservation=5G tank/home/bill
# zfs get reservation tank/home/bill NAME PROPERTY VALUE SOURCE
tank/home/bill reservation 5G local
NEW QUESTION 7
The storage pool configuration on your server is: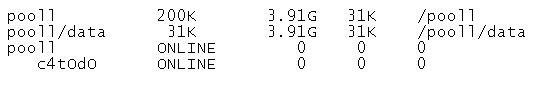
You back up the /pool1/data file system, creating a snapshot and copying that snapshot to tape (/dev/rmt/0). You perform a full backup on Sunday night and Incremental backups on Monday through Saturday night at 11:00 pm. Each incremental backup will copy only the data that has been modified since the Sunday backup was started.
On Thursday, at 10:00 am, you had a disk failure. You replaced the disk drive (c4t0d0). You created pool (pool1) on that disk.
Which option would you select to restore the data in the /pool1/data file system?
Answer: D
Explanation: First the full backup must be restored. This would be the Sunday backup.
Then the last incremental backup must be restored. This would be the Wednesday backup. Before restoring the Wednesday incremental file system snapshot, the most recent snapshot must first be rolled back.
By exclusion D) would be best answer even though it is incomplete.
NEW QUESTION 8
You are setting up an automated installer (AI) install server and issue the following command:
installadm create-service -n prod_ai -s /repo/prod_ai.iso
-i 192.168.1.100 -c 5 -d /export/repo
Which four options describe the install server that you have configured?
Answer: ABDF
Explanation: A: -n <svcname>
Uses this install service name instead of default service name.
B: -i <dhcp_ip_start>
Sets up a new DHCP server. The IP addresses, starting from dhcp_address_start, are set up.
D: -c <count_of_ipaddr>
Sets up a total number of IP addresses in the DHCP table equal to the value of the count_of_ipaddr. The first IP address is the value of dhcp_ip_start that is provided by the -i option.
F: -s <srcimage>
Specifies location of AI ISO image to use for setting up the install service.
<targetdir>
Required: Specifies location to set up net image.
NEW QUESTION 9
After installing the OS, the following network configuration information is displayed from the system:
Which option describes the state of this server?
Answer: C
Explanation: Only the loopback addresses are configured. No IP address is configured.
NEW QUESTION 10
A local repository is available on this system and you need to enable clients to access this repository via HTTP. The repository information is:
PUBLISHERTYPESTATUSURI
solarisoriginonlinehttp://sysA.example.com
Identify two of the steps that are required to make the local repository on this server available to the client via HTTP.
Answer: AE
Explanation: A: Configure the Repository Server Service
To enable clients to access the local repository via HTTP, enable the application/pkg/server Service Management Facility (SMF) service.
# svccfg -s application/pkg/server setprop pkg/inst_root=/export/repoSolaris11
# svccfg -s application/pkg/server setprop pkg/readonly=true
E: Use pkg.depotd to serve the repository to clients. Start the Repository Service
Restart the pkg.depotd repository service.
# svcadm refresh application/pkg/server
# svcadm enable application/pkg/server
To check whether the repository server is working, open a browser window on the localhost location.
NEW QUESTION 11
The line
set noexec_user_stack= l
should be added to the /etc/system file to prevent an executable stack while executing user programs. What is the purpose of this?
Answer: D
Explanation: How to Disable Programs From Using Executable Stacks Purpose: Prevent executable stack from overflowing. You must be in the root role.
Edit the /etc/system file, and add the following line: set noexec_user_stack=1
Reboot the system.
# reboot
NEW QUESTION 12
Which three options accurately describe Oracle Solaris 11 zones?
Answer: ADF
Explanation: A: Zones can use Oracle Solaris 11 products and features such as the following: Oracle Solaris ZFS encryption
Network virtualization and QoS CIFS and NFS
C: Non-global zones cannot modify the system clock by default, but each zone can have a separate time zone setting.
F (not E): The Oracle Solaris Zones partitioning technology is used to virtualize operating system services and provide an isolated and secure environment for running applications. A zone is a virtualized operating system environment created within a single instance of the Oracle Solaris operating system.
NEW QUESTION 13
Which five statements describe options available for installing the Oracle Solaris 11operating system using the installation media?
Answer: ABDFH
Explanation: A: If the network is setup to perform automated installations, you can perform a text installation over the network by setting up an install service on the network and selecting a text installation when the client system boots.
B: After a fresh install of Solaris 11 express, only the console mode is activated. To add Gnome, simply do :
$ sudo pkg install slim_install
This will install additional packages that are not installed by default. D: The text installer advantages over the GUI installer include:
* In addition to modifying partitions, the text installer enables you to create and modify VTOC slices within the Solaris partition.
F: How do I upgrade my Solaris 10 or lower systems to Solaris 11?
Unfortunately, you CAN'T. There is no direct upgrade installer or other tool that will allow you to upgrade from earlier releases of Solaris to Solaris 11. This is primarily due to the vast changes in the packaging mechanism in Solaris 10.
NEW QUESTION 14
Which two options accurately describe the network characteristics of a zone?
Answer: AB
Explanation: A: Non-global zones can not utilize DHCP (neither client nor server).
B (not C): By default, non-global zones will be configured with a shared IP functionality. What this means is that IP layer configuration and state is shared between the zone you’re creating and the global zone. This usually implies both zones being on the same IP subnet for each given NIC.
Note: A zone is a virtual operating system abstraction that provides a protected environment in which applications run. The applications are protected from each other to provide software fault isolation. To ease the labor of managing multiple applications and their environments, they co-exist within one operating system instance, and are usually managed as one entity.
The original operating environment, before any zones are created, is also called the "global zone" to distinguish it from non-global zones, The global zone is the operating system instance.
Incorrect Answer
E: Exclusive-IP zones can use IPMP. IPMP is configured the same way in an exclusive-IP zone as it is on a system not using zones.
For shared-IP zones, IPMP can be configured in the global zone. F: Full IP-level functionality is available in an exclusive-IP zone. An exclusive-IP zone has its own IP-related state.
An exclusive-IP zone is assigned its own set of data-links using the zonecfg command. The zone is given a data-link name such as xge0, e1000g1, or bge32001, using the physical property of the net resource. The address property of the net resource is not set.
Note that the assigned data-link enables the snoop command to be used.
The dladm command can be used with the show-linkprop subcommand to show the assignment of data-links to running exclusive-IP zones.
NEW QUESTION 15
When you issue the “gzip: zommand not found” message is displayed. You need to install the gzip utility on your system.
Which command would you use to check if the gzip utility is available from the default publisher for installation?
Answer: D
Explanation: Searching for Packages
Use the pkg search command to search for packages whose data matches the specified pattern.
Like the pkg contents command, the pkg search command examines the contents of packages. While the pkg contents command returns the contents, the pkg
search command returns the names of packages that match the query.
pkg search
search [-HIaflpr] [-o attribute ...] [-s repo_uri] query Search for matches to the query, and display the results.
Which tokens are indexed are action-dependent, but may include content hashes and pathnames.
Note: pkg is the retrieval client for the image packaging system. With a valid configuration, pkg can be invoked to create locations for packages to be installed, called 'images', and install packages into those images. Packages are published by publishers, who may make their packages available at one or more repositories. pkg, then, retrieves packages from a publisher's repository and installs them into an image.
NEW QUESTION 16
A user on the system has started a process, but it needs to be terminated. The process ID was determined as follows:
pgrep userprogram l5317
The user attempted to terminate the program as follows: pkill 15317
This command runs without an error message, and the process continues to run. What is the issue?
Answer: B
Explanation: You can use the pgrep and pkill commands to identify and stop command processes that you no longer want to run. These commands are useful when you mistakenly start a process that takes a long time to run.
To terminate a process:
Type pgrep to find out the PID(s) for the process(es). Type pkill followed by the PID(s).
You can kill any process that you own. Superuser can kill any process in the system except for those processes with process IDs of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4. Killing these processes most likely
will crash the system.
NEW QUESTION 17
The ZFS configuration on your server is:
Pool1 6.67G31K/pool Pool1/data31K31K/data
Select the three commands that you would use to 1. Create, 2. List, and 3. Delete a snapshot of the /data file system.
Answer: ADE
Explanation: A: Snapshots are created by using the zfs snapshot command, which takes as its only argument the name of the snapshot to create.
D: You can list snapshots as follows:
# zfs list -t snapshot
E: Snapshots are destroyed by using the zfs destroy command. For example:
# zfs destroy tank/home/ahrens@now
NEW QUESTION 18
In an effort to reduce storage space on your server, you would like to eliminate duplicate copies of data in your server’s ZFS file systems.
How do you specify that pool1/data should not contain duplicate data blocks (redundant data) on write operations?
Answer: E
Explanation: ZFS Deduplication Property
Solaris Express Community Edition, build 129: In this Solaris release, you can use the deduplication property to remove redundant data from your ZFS file systems. If a file system has the dedup property enabled, duplicate data blocks are removed synchronously. The result is that only unique data is stored and common components are shared between files.
You can enable this property as follows:
# zfs set dedup=on tank/home
NEW QUESTION 19
What is the result of executing the following command? svcs -d svc:/network/ssh:default
Answer: B
Explanation: The svcs command displays information about service instances as recorded in the service configuration repository.
-d Lists the services or service instances upon which the given service instances depend.
Recommend!! Get the Full 1Z0-821 dumps in VCE and PDF From Surepassexam, Welcome to Download: https://www.surepassexam.com/1Z0-821-exam-dumps.html (New 243 Q&As Version)